Node js rest api login with mysql and express js jwt auth; Through this tutorial, you will learn how to build user authentication REST Api in node.js + express + mysql with jwt.
JSON Web Tokens (JWT) are an RFC 7519 open industry standard for representing claims between two parties. For example, you can use jwt.io to decode, verify, and produce JWT. JWT specifies a compact and self-contained method for communicating information as a JSON object between two parties
Create Login REST API using Node.js + Express + MySQL
- Step 1 – Create Database and Table
- Step 2 – Create Node Express js App
- Step 3 – Connect App to Database
- Step 4 – Install express and required Modules
- Step 5 – Create Server.js File
- Step 6 – Create Validation.js, Router.js
- Step 7 – Start Node Express Js App Server
- Step 8 – Test Rest Apis with PostMan App
Step 1 – Create Database And Table
Execute the following command on terminal to create database and table:
CREATE DATABASE node-app
CREATE TABLE users (
id int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
name varchar(50) COLLATE utf8mb4_unicode_ci NOT NULL,
email varchar(50) COLLATE utf8mb4_unicode_ci NOT NULL,
password varchar(200) COLLATE utf8mb4_unicode_ci NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (id),
UNIQUE KEY email (email)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=4 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COLLATE=utf8mb4_unicode_ci;
Step 2 – Create Node Express js App
Execute the following command on terminal to create node js app:
mkdir nodejs-auth-rest-api-mysql cd nodejs-auth-rest-api-mysql npm init -y
Step 3 – Connect App to Database
Create dbConnection.js file into your app root directory add the following code into it to connect your node js express app to database:
var mysql = require('mysql');
var conn = mysql.createConnection({
host: 'localhost', // Replace with your host name
user: 'root', // Replace with your database username
password: '', // Replace with your database password
database: 'my-node' // // Replace with your database Name
});
conn.connect(function(err) {
if (err) throw err;
console.log('Database is connected successfully !');
});
module.exports = conn;
Step 4 – Install express and required Modules
Execute the following command on terminal to install express express-validator mysql body-parser jsonwebtoken bcryptjs cors into your node js express app:
npm install express express-validator mysql body-parser jsonwebtoken bcryptjs cors --save
- Express — Express is a minimal and flexible Node.js web application framework that provides a robust set of features for web and mobile applications.
- Express-validator — Express Validator is a set of Express. js middleware that wraps validator. js , a library that provides validator and sanitizer functions. Simply said, Express Validator is an Express middleware library that you can incorporate in your apps for server-side data validation.
- MySQL — MySQL an open-source relational database management system (RDBMS).
- body-parser — Express body-parser is an npm library used to process data sent through an HTTP request body. It exposes four express middlewares for parsing text, JSON, url-encoded and raw data set through an HTTP request body.
- jsonwebtoken — This module provides Express middleware for validating JWTs (JSON Web Tokens) through the jsonwebtoken module. The decoded JWT payload is available on the request object.
- bcryptjs — The bcrypt hashing function allows us to build a password security platform that scales with computation power and always hashes every password with a salt.
- cors — CORS is a node.js package for providing a Connect/Express middleware that can be used to enable CORS with various options.
Step 5 – Create Server.js File
Create server.js file and import express express-validator mysql body-parser jsonwebtoken bcryptjs cors into your server.js file; as shown below:
const createError = require('http-errors');
const express = require('express');
const path = require('path');
const bodyParser = require('body-parser');
const cors = require('cors');
const indexRouter = require('./router.js');
const app = express();
app.use(express.json());
app.use(bodyParser.json());
app.use(bodyParser.urlencoded({
extended: true
}));
app.use(cors());
app.use('/api', indexRouter);
// Handling Errors
app.use((err, req, res, next) => {
// console.log(err);
err.statusCode = err.statusCode || 500;
err.message = err.message || "Internal Server Error";
res.status(err.statusCode).json({
message: err.message,
});
});
app.listen(3000,() => console.log('Server is running on port 3000'));
Step 6 – Create Validation.js, Router.js and dbConnection.js
Create validation.js and router.js. So visit your app root directory and create this files.
Then add the following code into your validation.js file:
const { check } = require('express-validator');
exports.loginValidation = [
check('email', 'Please include a valid email').isEmail().normalizeEmail({ gmail_remove_dots: true }),
check('password', 'Password must be 6 or more characters').isLength({ min: 6 })
]
Then add the following code into your router.js file:
const express = require('express');
const router = express.Router();
const db = require('./dbConnection');
const { signupValidation, loginValidation } = require('./validation');
const { validationResult } = require('express-validator');
const bcrypt = require('bcryptjs');
const jwt = require('jsonwebtoken');
router.post('/login', loginValidation, (req, res, next) => {
db.query(
`SELECT * FROM users WHERE email = ${db.escape(req.body.email)};`,
(err, result) => {
// user does not exists
if (err) {
throw err;
return res.status(400).send({
msg: err
});
}
if (!result.length) {
return res.status(401).send({
msg: 'Email or password is incorrect!'
});
}
// check password
bcrypt.compare(
req.body.password,
result[0]['password'],
(bErr, bResult) => {
// wrong password
if (bErr) {
throw bErr;
return res.status(401).send({
msg: 'Email or password is incorrect!'
});
}
if (bResult) {
const token = jwt.sign({id:result[0].id},'the-super-strong-secrect',{ expiresIn: '1h' });
db.query(
`UPDATE users SET last_login = now() WHERE id = '${result[0].id}'`
);
return res.status(200).send({
msg: 'Logged in!',
token,
user: result[0]
});
}
return res.status(401).send({
msg: 'Username or password is incorrect!'
});
}
);
}
);
});
module.exports = router;
- login route – When you call this route on postman app with email and password; it will return jwt token. Which is used to call get-user method.
Step 7 – Start Node Express Js App Server
Execute the following command on terminal to start node express js server:
//run the below command nodemon server.js after run this command open your browser and hit http://127.0.0.1:3000/api/login
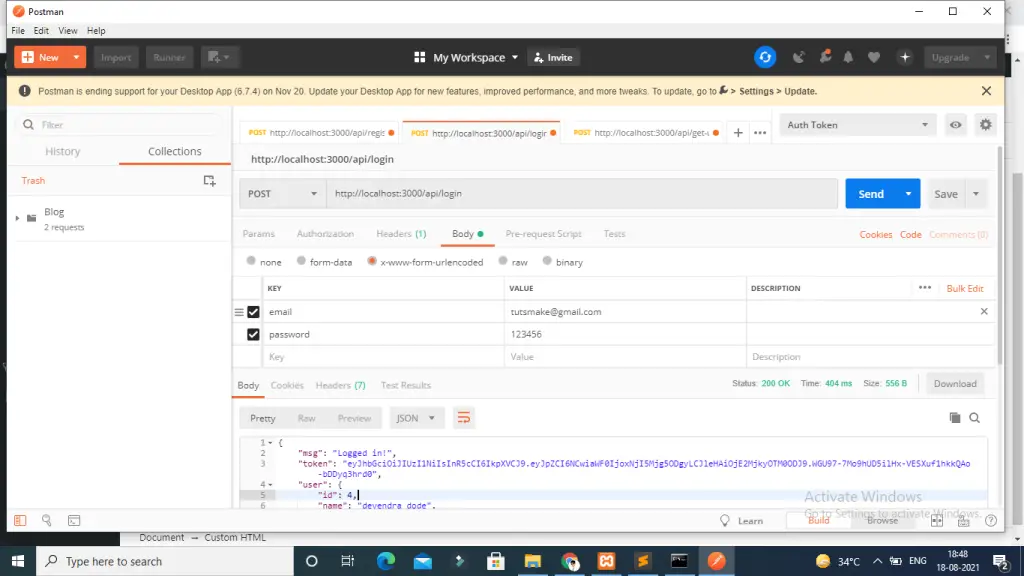
Step 8 – Test Rest Apis with PostMan App
Test node js experss + mysql user login api with Postman app:
Test node js experss + mysql user login api with Postman app:
POST - http://localhost:3000/api/login
Conclusion
node js rest api login with mysql and express js jwt auth; Through this tutorial, you have learned how to build user authentication REST Api in node.js + express + mysql with jwt.




